What is a Layer 3 MPLS VPN and why to use it?
Layer 3, or VPRN (virtual private routed network), utilizes layer 3 VRF (VPN/virtual routing and forwarding) to segment routing tables for each customer utilizing the service. The customer peers with the service provider router and the two exchange routes, which are placed into a routing table specific to the customer. Multiprotocol BGP (MP-BGP) is required in the cloud to utilize the service, which increases complexity of design and implementation. L3 VPNs are typically not deployed on utility networks due to their complexity; however, a L3 VPN could be used to route traffic between corporate or datacenter locations.
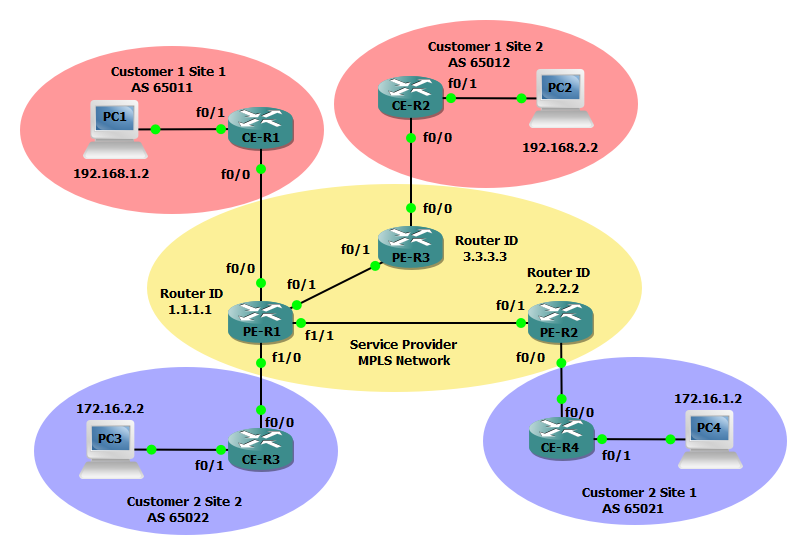
In the example below we will configure three MPLS service provider routers (PEs), two routers for customer 1 (CE), and two additional routers for Customer 2 (CE). The service provider MPLS network will run a basic OSPF configuration and all customer routers will participate in BGP to reach their other sites. Both customer 1 and customer 2 must be provisioned a VRF instance to facilitate a virtual private network across the MPLS cloud.
Steps to configure a Layer 3 MPLS VPN
PE-R1(config)#interface Loopback0 PE-R1(config-if)#ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 ! PE-R1(config)#interface FastEthernet0/1 PE-R1(config-if)#ip address 13.13.13.1 255.255.255.252 PE-R1(config-if)#mpls ip ! PE-R1(config)#interface FastEthernet1/1 PE-R1(config-if)#ip address 23.23.23.2 255.255.255.252 PE-R1(config-if)#mpls ip ! PE-R1(config)#router ospf 100 PE-R1(config-router)#router-id 1.1.1.1 PE-R1(config-router)#network 1.1.1.1 0.0.0.0 area 0 PE-R1(config-router)#network 13.13.13.0 0.0.0.3 area 0 PE-R1(config-router)#network 23.23.23.0 0.0.0.3 area 0
PE-R2(config)#interface Loopback0 PE-R2(config-if)#ip address 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.255 ! PE-R2(config)#interface FastEthernet0/1 PE-R2(config-if)#ip address 23.23.23.1 255.255.255.252 PE-R2(config-if)#mpls ip ! PE-R2(config)#router ospf 100 PE-R2(config)#router-id 2.2.2.2 PE-R2(config)#network 2.2.2.2 0.0.0.0 area 0 PE-R2(config)#network 23.23.23.0 0.0.0.3 area 0
PE-R3(config)#interface Loopback0 PE-R3(config-if)#ip address 3.3.3.3 255.255.255.255 ! PE-R3(config)#interface FastEthernet0/1 PE-R3(config-if)#ip address 13.13.13.2 255.255.255.252 PE-R3(config-if)#mpls ip ! PE-R3(config)#router ospf 100 PE-R3(config-router)#router-id 3.3.3.3 PE-R3(config-router)#network 3.3.3.3 0.0.0.0 area 0 PE-R3(config-router)#network 13.13.13.0 0.0.0.3 area 0
Step 2: Forcibly change the LDP router id on PE-R1, PE-R2, and PE-R3.
PE-R1(config)#mpls ldp router-id Loopback0 force
PE-R2(config)#mpls ldp router-id Loopback0 force
PE-R3(config)#mpls ldp router-id Loopback0 force
Step 3: Configure vrf vpn-101 for Customer 1 on PE-R1 and vrf vpn-102 for Customer 2 PE-R3 and PE-R1 and PE-R2. We will also enable the VRF on the applicable interfaces and configure an IP address on the interfaces as well.
PE-R1(config)#ip vrf vpn-101 PE-R1(config-vrf)#rd 65000:101 PE-R1(config-vrf)#route-target export 65000:101 PE-R1(config-vrf)#route-target import 65000:101 ! PE-R1(config)#ip vrf vpn-102 PE-R1(config-vrf)#rd 65000:102 PE-R1(config-vrf)#route-target export 65000:102 PE-R1(config-vrf)#route-target import 65000:102 ! PE-R1(config)#interface FastEthernet0/0 PE-R1(config-if)#ip vrf forwarding vpn-101 PE-R1(config-if)#ip address 10.1.0.1 255.255.255.252 ! PE-R1(config)#interface FastEthernet1/0 PE-R1(config-if)#ip vrf forwarding vpn-102 PE-R1(config-if)#ip address 10.3.0.1 255.255.255.0
PE-R2(config)#ip vrf vpn-102 PE-R2(config-vrf)#rd 65000:102 PE-R2(config-vrf)#route-target export 65000:102 PE-R2(config-vrf)#route-target import 65000:102 ! PE-R2(config)#interface FastEthernet0/0 PE-R2(config-if)#ip vrf forwarding vpn-102 PE-R2(config-if)#ip address 10.4.0.1 255.255.255.0
PE-R3(config)#ip vrf vpn-101 PE-R3(config-vrf)#rd 65000:101 PE-R3(config-vrf)#route-target export 65000:101 PE-R3(config-vrf)#route-target import 65000:101 ! PE-R3(config)#interface FastEthernet0/0 PE-R3(config-if)#ip vrf forwarding vpn-101 PE-R3(config-if)#ip address 10.2.0.1 255.255.255.252
Step 4: Next configure a BGP process on PE-R1, PE-R2, and PE-R3 to facilitate advertisements of customer networks over the MPLS network.
PE-R1(config)#router bgp 65000 PE-R1(config-router)#bgp log-neighbor-changes PE-R1(config-router)#neighbor 2.2.2.2 remote-as 65000 PE-R1(config-router)#neighbor 2.2.2.2 update-source Loopback0 PE-R1(config-router)#neighbor 3.3.3.3 remote-as 65000 PE-R1(config-router)#neighbor 3.3.3.3 update-source Loopback0 ! PE-R1(config-router)#address-family vpnv4 PE-R1(config-router-af)#neighbor 2.2.2.2 activate PE-R1(config-router-af)#neighbor 2.2.2.2 send-community extended PE-R1(config-router-af)#neighbor 3.3.3.3 activate PE-R1(config-router-af)#neighbor 3.3.3.3 send-community extended ! PE-R1(config-router)#address-family ipv4 vrf vpn-101 PE-R1(config-router-af)#redistribute connected PE-R1(config-router-af)#neighbor 10.1.0.2 remote-as 65011 PE-R1(config-router-af)#neighbor 10.1.0.2 activate ! PE-R1(config-router)#address-family ipv4 vrf vpn-102 PE-R1(config-router-af)#redistribute connected PE-R1(config-router-af)#neighbor 10.3.0.2 remote-as 65022 PE-R1(config-router-af)#neighbor 10.3.0.2 activate
PE-R2(config)#router bgp 65000 PE-R2(config-router)#bgp log-neighbor-changes PE-R2(config-router)#neighbor 1.1.1.1 remote-as 65000 PE-R2(config-router)#neighbor 1.1.1.1 update-source Loopback0 ! PE-R2(config-router)#address-family vpnv4 PE-R2(config-router-af)#neighbor 1.1.1.1 activate PE-R2(config-router-af)#neighbor 1.1.1.1 send-community extended ! PE-R2(config-router)#address-family ipv4 vrf vpn-102 PE-R2(config-router-af)#redistribute connected PE-R2(config-router-af)#neighbor 10.4.0.2 remote-as 65021 PE-R2(config-router-af)#neighbor 10.4.0.2 activate
PE-R3(config)#router bgp 65000 PE-R3(config-router)#bgp log-neighbor-changes PE-R3(config-router)#neighbor 1.1.1.1 remote-as 65000 PE-R3(config-router)#neighbor 1.1.1.1 update-source Loopback0 ! PE-R3(config-router)#address-family vpnv4 PE-R3(config-router-af)#neighbor 1.1.1.1 activate PE-R3(config-router-af)#neighbor 1.1.1.1 send-community extended ! PE-R3(config-router)#address-family ipv4 vrf vpn-101 PE-R3(config-router-af)#redistribute connected PE-R3(config-router-af)#neighbor 10.2.0.2 remote-as 65012 PE-R3(config-router-af)#neighbor 10.2.0.2 activate
Steps to configure Customer 1 CE devices
CE-R1(config)#interface FastEthernet0/0 CE-R1(config-if)#ip address 10.1.0.2 255.255.255.252 ! CE-R1(config-if)#interface FastEthernet0/1 CE-R1(config-if)#ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 ! CE-R1(config-if)#router bgp 65011 CE-R1(config-router)#bgp log-neighbor-changes CE-R1(config-router)#network 10.1.0.0 mask 255.255.255.252 CE-R1(config-router)#network 192.168.1.0 CE-R1(config-router)#neighbor 10.1.0.1 remote-as 65000
CE-R2(config)#interface FastEthernet0/0 CE-R2(config-if)#ip address 10.2.0.2 255.255.255.252 ! CE-R2(config-if)#interface FastEthernet0/1 CE-R2(config-if)#ip address 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0 ! CE-R2(config-if)#router bgp 65012 CE-R2(config-router)#bgp log-neighbor-changes CE-R2(config-router)#network 10.2.0.0 mask 255.255.255.252 CE-R2(config-router)#network 192.168.2.0 CE-R2(config-router)#neighbor 10.2.0.1 remote-as 65000
Steps to configure Customer 2 CE devices
CE-R3(config)#interface FastEthernet0/0 CE-R3(config-if)#ip address 10.3.0.2 255.255.255.0 ! CE-R3(config-if)#interface FastEthernet0/1 CE-R3(config-if)#ip address 172.16.2.1 255.255.255.0 ! CE-R3(config-if)#router bgp 65022 CE-R3(config-router)#bgp log-neighbor-changes CE-R3(config-router)#network 10.3.0.0 mask 255.255.255.0 CE-R3(config-router)#network 172.16.2.0 mask 255.255.255.0 CE-R3(config-router)#neighbor 10.3.0.1 remote-as 65000
CE-R4(config)#interface FastEthernet0/0 CE-R4(config-if)#ip address 10.4.0.2 255.255.255.0 ! CE-R4(config-if)#interface FastEthernet0/1 CE-R4(config-if)#ip address 172.16.1.1 255.255.255.0 ! CE-R4(config-if)#router bgp 65021 CE-R4(config-router)#bgp log-neighbor-changes CE-R4(config-router)#network 10.4.0.0 mask 255.255.255.0 CE-R4(config-router)#network 172.16.1.0 mask 255.255.255.0 CE-R4(config-router)#neighbor 10.4.0.1 remote-as 65000
Verify the configuration
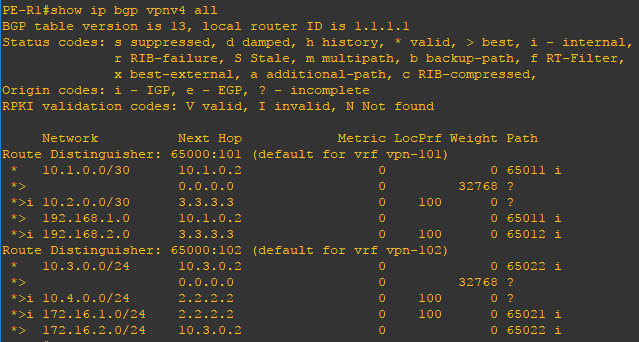
Now that the configuration is finished lets verify our neighbors and routes. Using the show ip bgp vpnv4 all command you can verify the BGP routes distributed and to which VRF they belong.
Using the show mpls forwarding-table command you can verify the mpls topology.